Using AWS Secrets Manager with Amazon EKS for Secure Secrets Management

Managing sensitive credentials like database passwords, API keys, or authentication tokens in Kubernetes is a critical aspect of application security. By integrating AWS Secrets Manager with Amazon EKS, you can securely store and retrieve secrets for your applications while following best practices for access control and automation.
This blog will guide you through setting up an Amazon EKS cluster, integrating AWS Secrets Manager, and deploying a sample application to demonstrate secure secret retrieval.
What You’ll Learn
- How to set up an Amazon EKS cluster.
- How to store and manage sensitive information in AWS Secrets Manager.
- How to integrate AWS Secrets Manager with Kubernetes using IAM Roles for Service Accounts (IRSA).
- How to deploy a sample application in EKS that retrieves secrets dynamically at runtime.
Step 1: Set Up an Amazon EKS Cluster
1. Create the EKS Cluster
Run the following command to create an EKS cluster:
eksctl create cluster \
–name demo-eks-cluster \
–region us-east-1 \
–nodegroup-name std-workers \
–node-type t3.medium \
–nodes 2 \
–nodes-min 1 \
–nodes-max 3 \
–managed
This command creates an EKS cluster with a managed node group in the us-east-1 region.
2. Verify the Cluster
Ensure the cluster was created successfully:
eksctl get cluster –region us-east-1
![]()
3. Update kubeconfig
Update the kubeconfig file to connect kubectl to your EKS cluster:
aws eks –region us-east-1 update-kubeconfig –name demo-eks-cluster
4. Verify Node Readiness
Check if the worker nodes are ready:
kubectl get nodes
You should see the nodes in the Ready state.

Step 2: Store Secrets in AWS Secrets Manager
1. Create a Secret
Example: RambunctDatabaseSecret
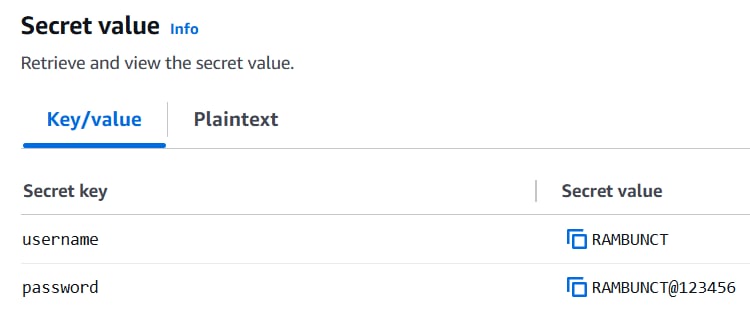
2. Copy the Secret ARN
After saving the secret, copy the ARN for use in the IAM role permissions.
Step 3: Enable IAM Roles for Service Accounts (IRSA)
1. Associate OIDC Provider
Enable IAM Roles for Service Accounts (IRSA) by associating an OIDC provider with your cluster:
eksctl utils associate-iam-oidc-provider –region us-east-1 –cluster demo-eks-cluster –approve
2. Verify OIDC Provider
Check if the OIDC provider is correctly associated:
aws eks describe-cluster –name demo-eks-cluster –query “cluster.identity.oidc.issuer” –output text
The output should resemble:
https://oidc.eks.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/id/<oidc-id>
Step 4: Create IAM Role with Secret Access
1. Create IAM Policy
Save the following JSON policy as secrets-access-policy.json:
{
“Version”: “2012-10-17”,
“Statement”: [
{
“Effect”: “Allow”,
“Action”: [
“secretsmanager:ListSecrets”,
“secretsmanager:GetSecretValue”
],
“Resource”: [
“arn:aws:secretsmanager:us-east-1:<account-id>:secret:RambunctDatabaseSecret*”
]
}
]
}
Replace <account-id> with your AWS account ID.
2. Create IAM Role
1. Save this trust policy as trust-policy.json:
{
“Version”: “2012-10-17”,
“Statement”: [
{
“Effect”: “Allow”,
“Principal”: {
“Federated”: “arn:aws:iam::<account-id>:oidc-provider/oidc.eks.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/id/<oidc-id>”
},
“Action”: “sts:AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity”,
“Condition”: {
“StringEquals”: {
“oidc.eks.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/id/<oidc-id>:sub”: “system:serviceaccount:default:my-app-sa”
}
}
}
]
}
2.Create the role and attach the policy:
aws iam create-role –role-name eks-secret-access-role \–assume-role-policy-document file://trust-policy.json
aws iam put-role-policy –role-name eks-secret-access-role \
–policy-name secrets-access-policy \
–policy-document file://secrets-access-policy.json
Step 5: Create Kubernetes Service Account
1.Save the following YAML as service-account.yaml:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: my-app-sa
namespace: default
annotations:
eks.amazonaws.com/role-arn: arn:aws:iam::<account-id>:role/eks-secret-access-role
2. Apply the service account:
kubectl apply -f service-account.yaml
Step 6: Deploy the Application
1. Create Python Script
Save the following script as app.py:
import boto3
import json
def get_secret(secret_name, region_name=”us-east-1″):
client = boto3.client(“secretsmanager”, region_name=region_name)
try:
response = client.get_secret_value(SecretId=secret_name)
return response[“SecretString”] if “SecretString” in response else response[“SecretBinary”]
except Exception as e:
print(f”Error retrieving secret: {e}”)
return None
if __name__ == “__main__”:
secret_name = “MyAppDatabaseSecret”
secret = get_secret(secret_name)
if secret:
print(f”Fetched secret: {secret}”)
else:
print(“Failed to fetch secret”)
2. Create ConfigMap
Store the script in a Kubernetes ConfigMap:
kubectl create configmap app-script –from-file=app.py
3. Create Deployment
Save the following YAML as deployment.yaml:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: my-app
labels:
app: my-app
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: my-app
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: my-app
spec:
serviceAccountName: my-app-sa
containers:
– name: python-app
image: python:3.9-slim
command: [“/bin/sh”, “-c”]
args:
– >
pip install boto3 &&
python /app/app.py;
volumeMounts:
– name: app-script
mountPath: /app
env:
– name: AWS_REGION
value: us-east-1
volumes:
– name: app-script
configMap:
name: app-script
3. Apply the deployment:
kubectl apply -f deployment.yaml
Step 7: Verify the Application
- Check the pod:
kubectl get pods

- View the logs:
kubectl logs <pod-name>
The logs should display the secret retrieved from AWS Secrets Manager.
![]()
Conclusion
By following this guide, you’ve set up an EKS cluster, securely stored a secret in AWS Secrets Manager, and deployed an application that fetches the secret dynamically using IRSA. This workflow ensures that sensitive information is securely managed and accessed in a Kubernetes environment.